ADAS: Futuristic Features for Safety & Beyond
In the United States, fatal vehicle accidents have risen significantly over the last several years, and in 2022, there were an average of 117 fatal crashes per day.
Enter the advanced driver assistance system (ADAS). Designed to save lives and reduce accidents caused by human error, ADAS brings together several innovative features and technologies to provide a 360-degree view of the vehicle’s surroundings. These advanced and intuitive functions improve reaction times, alert drivers of hazardous conditions, and sometimes perform fully autonomous adjustments.
Several Features, One Goal
ADAS combines multiple sensing technologies, including radar, ultrasound, LIDAR, and cameras, to enhance driver and passenger safety from every angle. The exact features will vary by vehicle make and model. Available ADAS functions include:
- Adaptive cruise control (ACC) - maintains a set distance from the vehicle and the car in front of it
- Adaptive high beam control (AHBC) - switches headlights to high or low beams depending on traffic and light conditions
- Automatic emergency braking (AEB) - applies brakes to avoid a front collision with a vehicle or pedestrian
- Automatic parking system (APS) - automatically steers, brakes, and accelerates the vehicle into a parking spot
- Blind spot detection (BSD) - notifies driver of vehicles in the blind spots
- Collision avoidance system (CAS) - provides real-time audio and visual alerts and assists drivers to avoid imminent danger
- Cross-traffic alert (CTA) - alerts driver to vehicles crossing behind the vehicle when it’s in reverse
- Drowsy driver detection (DDD) - alerts driver when they are showing signs of drowsiness
- Driver monitoring system (DMS) - monitors driver’s attention level and alerts them if they are drowsy or distracted
- Emergency driver assist (EDA) - helps control vehicle if the driver is incapacitated
- Forward collision warning (FCW) - alerts drivers to potential collisions with vehicles or objects ahead
- Head-up display (HUD) - projects important information such as navigation and warnings onto the windshield so the drivers don’t have to take their eyes off the road
- Highway assist (HA) - provides limited self-driving capability on highways
- Intelligent speed adaptation (ISA) - uses information about the road and traffic to automatically adjust the vehicle's speed to the legal speed limit or a safe speed, whichever is lower
- Lane change assist (LCA) - helps driver change lanes safely
- Lane departure warning (LDW) - alerts driver when the vehicle is drifting out of its lane
- Lane keeping assistance (LKA) - gently steers vehicle back into its lane if it is drifting out
- Night vision system (NVS) - infrared cameras provide a view of the road ahead in low-light conditions
- Predictive cruise control - evaluates road conditions and adjusts vehicle speed automatically
- Rain-sensing wipers - automatically activate the wipers when rain is detected
- Surround view system (SVS) - delivers a 360-degree view of the vehicle’s surroundings
- Tire pressure monitoring system (TPMS) - notifies driver if the tire pressure gets low
- Traffic jam assist (TJA) - uses adaptive cruise control and lane keeping assist to automatically steer and accelerate/decelerate the vehicle in traffic jams
- Traffic sign recognition (TSR) - recognizes and displays traffic signs to the driver
- Turning assistant (TA) - helps the driver turn safely by steering and braking automatically
- Vehicular communication system (V2X) - enables vehicles to communicate with each other and the infrastructure to improve safety
- Wrong way driving warning (WWDW) - notifies driver if they are going in the wrong direction on a one-way road
How do advanced driver assistance systems work?
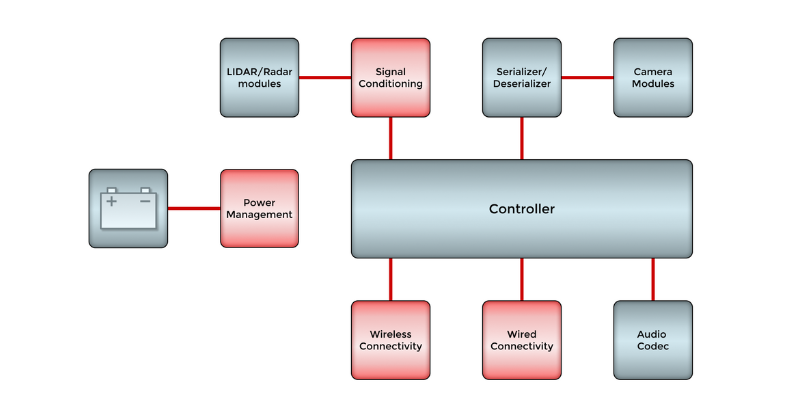
Multiple systems, including radar, imaging, LIDAR, ultrasound, cameras, and the instrument cluster, process their own inputs in dedicated microcontroller units (MCUs), which direct their outputs.
A serializer/deserializer circuit converts many streams of data (parallel data) into a one-bit stream to be transmitted over a high-speed connection. A receiver then converts the one-bit, or serial data back to the parallel data to be translated.
The various systems’ circuits are connected to a bus. Data is sent to the bus and the instrument panel as actions are executed.
Wired and wireless connections, including CAN, LIN, FlexRay, and ethernet help the system communicate desired actions.
Efficient power management of the radar transceiver, transmitter, and receiver is essential as the inputs reach the controller for processing.
The block diagram below demonstrates how the radar sensing module works and the discrete semiconductors needed for effective operation.
Block Diagram
Design Considerations
ADAS sensor modules are the brains of the 360-degree safety system. To design them effectively, engineers should factor in the following:
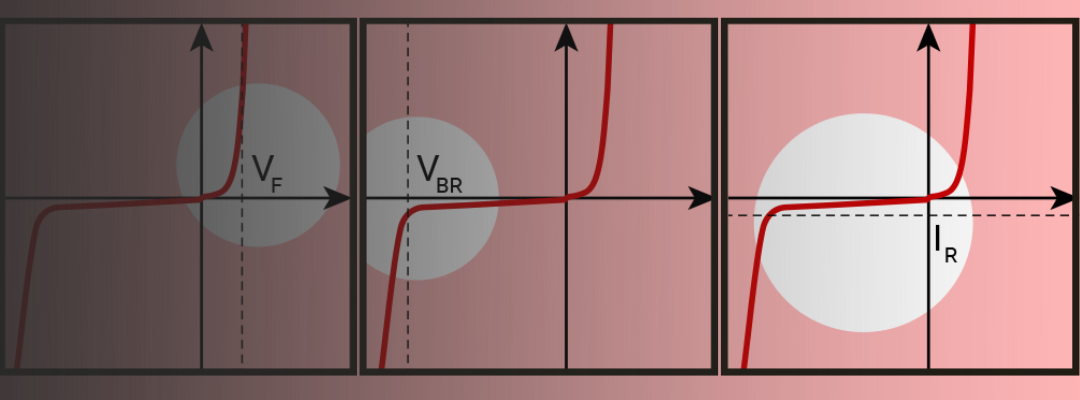
- ESD protection - components should be in place to safeguard against electrostatic discharge
- Component size - because multiple radar and sensors are needed to provide a complete view of the vehicle, there isn’t much space for all of the required components
- Reliability in harsh conditions - ADAS features enhance safety, so they must perform without failure in various automotive conditions
- Reverse battery protection - the design should account for damaging reverse polarity
- Thermal performance - with several systems working together in a small space, excess heat is not safe or efficient
- Efficiency - minimizing power losses at every function within various ADAS features is essential
- Cost - several sensing systems and technologies are required for ADAS to work together, so keeping component costs reasonable is imperative
- Applicable industry standards - all components should meet the requirements for automotive parts, including AEC-Q101
Recommended Products
Power Management |
|||
TVS: SMF24AQ
|
TVS: SMF36AQ
|
TVS: SMA6J24AQ
|
TVS: SMA6J36AQ
|
TVS: SMBJ24AQ
|
TVS: SMBJ36AQ
|
TVS: SMCJ24CAQ
|
TVS: SMCJ36AQ
|
Schottky Barrier Rectifier: SMD34PLQ
|
Schottky Barrier Rectifier: SMD36PLQ
|
Schottky Barrier Rectifier: SK36AQ-L
|
Schottky Barrier Rectifier: SK36BQ-L
|
Schottky Barrier Rectifier: SK36Q
|
|
|
|
Wired Connectivity |
|||
ESD Protection: ESD1524D3BHE3A
|
ESD Protection: ESD24VD3BHE3
|
ESD Protection: ESD27VD3BHE3
|
ESD Protection: ESDSBL5V0D5BHE3
|
ESD Protection: ESDULC5V0LBHE3
|
ESD Protection: ESDULC3V3LBHE3
|
|
|
Wireless Connectivity |
|||
ESD Protection: ESDSBL5V0D5BHE3
|
ESD Protection:ESDULC5V0LBHE3
|
ESD Protection: ESDULC3V3LBHE3
|
|
Signal Conditioning |
|||
ESD Protection: ESDSBL5V0D5BHE3
|
ESD Protection: ESDULC5V0LBHE3
|
ESD Protection: ESDULC3V3LBHE3
|
|
Advanced driver assistance systems use technology to reduce human error while driving and save lives. As vehicles continue to become more autonomous, reliable technology will be more important than ever. MCC Semi is proud to consistently deliver reliable components for all automotive applications.
Explore MCC’s diverse solutions for autos and EVs, including:
Interior Lighting
Exterior Lighting
Infotainment
Instrument Cluster
On-board Charger (OBC)
EV Charging Station
Battery Management System (BMS)
DC-DC Converter
Electric Power Steering (EPS)
Body Control Module (BCM)
Seat Control
Ready to chat or request a sample? Use the MCC website chatbot to contact us today.
.png?width=50&height=50&name=mcc%20150x150%20(1).png)