Designing for Real-time Reliability
Automotive instrument clusters display mission-critical data for safe operation, ranging from the status of vehicle systems to driving conditions. These dashboard data centers can be as simple as a series of gauges or as complex as hybrid 2D and 3D systems.
Instrument clusters enable communication between driver and machine using an interface fitted into the dashboard to showcase a myriad of crucial metrics to the driver. The interfaces and the metrics they display will vary by vehicle, and likely include:
- Speedometer - how fast the vehicle is currently driving
- Tachometer - the engine’s revolutions per minute (RPMs)
- Odometer - lifetime mileage of the vehicle to date
- Fuel gauge - how much gas is left in the tank
- Trip odometer - distance from Point A to Point B
- Temperature gauge - current temp of engine’s coolant
- Warning lights - alarms for issues with engine temperature, oil levels, tire pressure, airbags, anti-lock brakes, engine, seatbelt, or battery
- Indicator lights - status indication for turn signals, driving gear, and more
Additional data that may be included in some instrument clusters:
- Miles per gallon/fuel economy - current MPG rating
- Remaining driving range - how long before the vehicle needs to refuel or recharge
- Clock - current time displayed on the dashboard
- Temperature - current outdoor temperature
While the above features represent a wide array of potential displays, not all are required in every vehicle. Specific symbols, especially those not related to speed, battery, and ODO, must adhere to strict guidelines set by regulatory bodies. In many regions, these symbols are governed by authoritative entities, ensuring uniformity and compliance. These standards mean that certain symbols cannot be modified or omitted, underscoring their importance in the design process. This adherence to regulation ensures that drivers receive consistent and reliable information across different vehicles, enhancing both safety and usability.
How do instrument clusters work?
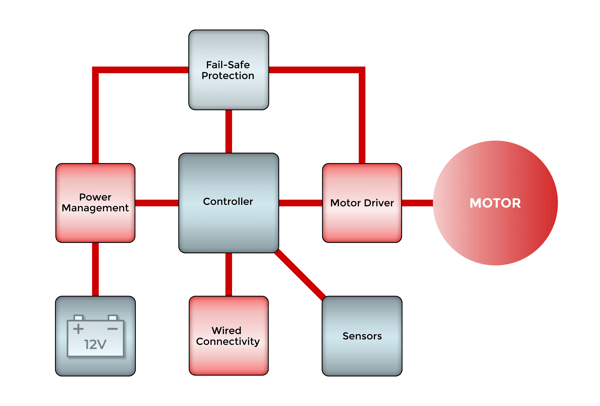
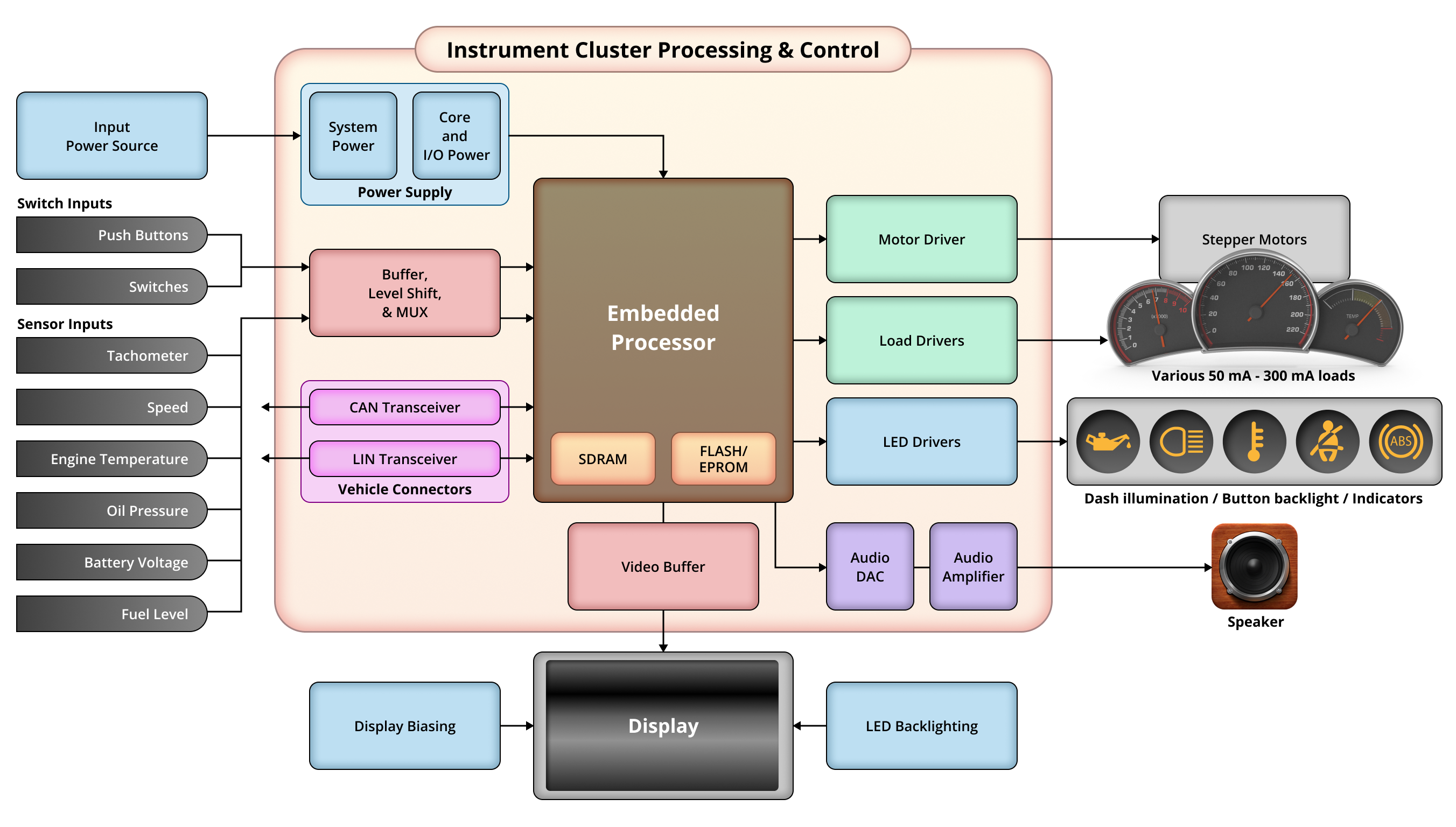
Dashboards or instrument clusters are made up of several switch inputs and sensors for various functions. These inputs, such as the tachometer, fuel gauge, odometer, temperature, speedometer, and other parameters are connected to a multiplexer (MUX), which provides inputs to the processor/controller.
As the brains of the operation, the controller processes these inputs and then utilizes LED drivers, load drivers, motor drivers, stepper motors, and audio DAC to transmit data to the dashboard featuring a series of indicators, backlit LED screens, and illuminated gauges.
CAN and LIN transceivers enable connectivity to help protect the device from ESD or overvoltage.
A wiring harness connects the instrument cluster to the electronic control unit (ECU) or controller.
All of these functions must take place in real time to maintain driver safety.
Enhancing Vehicle Interface Designs with Digital Instrument Clusters
Digital instrument clusters are revolutionizing vehicle dashboards, offering a seamless blend of technology and design to elevate user experience. Here's how they improve vehicle interface designs:
- Customization and Flexibility With digital clusters, drivers can enjoy a tailored experience. Unlike traditional dashboards, digital clusters provide configurable displays, allowing users to choose what information is most relevant—whether it's navigation, performance metrics, or multimedia options. This customization aligns with user preferences and enhances driving satisfaction.
- Advanced Display Technology Modern digital clusters utilize cutting-edge LCD screens, known for their clarity and vibrant colors, providing easy-to-read information even in adverse lighting conditions. This high-definition display ensures critical data is accessible at a glance, boosting both safety and convenience.
- Streamlined Integration The integration of digital clusters with vehicle systems is seamless, offering a holistic approach to displaying information. They work harmoniously with the vehicle's software, ensuring smooth operation and reduced latency. This integration supports real-time updates and can easily incorporate new features through software enhancements.
- Enhanced User Interface Digital clusters offer intuitive interfaces that simplify interactions. By consolidating multiple functions into a single display, they reduce the clutter associated with physical dials and buttons. This minimalist approach not only enhances aesthetic appeal but also improves functionality by guiding the driver’s focus intuitively.
- Future-Proofing and Upgradability Adopting a digital approach to instrument clusters means vehicles can be future-proofed. Software-driven clusters allow easy updates and the introduction of new features without requiring hardware changes, ensuring the vehicle remains contemporary with evolving technological standards.
By prioritizing user-centric design, digital clusters not only enhance the aesthetic quality of vehicle interiors but also improve operational efficiency and user interaction. Many brands are already demonstrating the potential of this technology, setting a new benchmark for automotive excellence.
Cabin Sensing: Enhancing Safety and Comfort Inside the Vehicle
As vehicles grow smarter, cabin sensing technology is becoming a key enabler of both safety and comfort. Using a combination of sensors, cameras, and AI-driven software, these systems can monitor driver attention levels, detect drowsiness, and help prevent accidents caused by distraction or fatigue.
But the benefits don’t stop at safety. Cabin sensing also supports convenience features that adjust the in-vehicle environment automatically—climate, seating, and lighting can all be tailored to individual preferences without the driver lifting a finger.
OEMs already report improved driver response times and higher passenger satisfaction where these technologies are in use. With ongoing advancements, cabin sensing is expected to move from high-end options to standard equipment across a wider range of vehicles, contributing to a more personalized and secure driving experience.
Automotive Instrument Panel Block Diagram
Engineering Tips
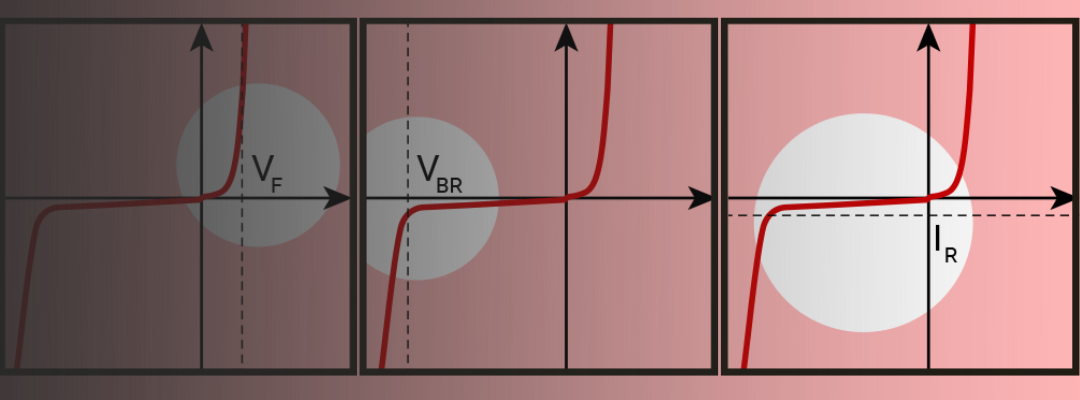
- Power Management TVS - reverse working maximum voltage (VRWM) should be higher than the supply voltage (V supply)
- Power Management Schottky Barrier Rectifier - at minimum, you need twice the output voltage of the switch-mode power supply (SMPS)
- Output Drivers - the drain-source voltage (VDS) must be at least twice the V supply
Design Considerations
When designing automotive instrument clusters, numerous factors must be taken into account to ensure optimal performance and safety. These considerations address various aspects such as efficiency, reliability, and adherence to industry standards, all crucial for meeting the demanding conditions of automotive applications. Below is a detailed list of these considerations:
- Efficient Power Management: Minimizing losses and enhancing efficiency is essential for all components powered by the vehicle’s battery, including the instrument cluster.
- Reliability in Harsh Conditions: Designs must be able to withstand a range of operating conditions commonly found in auto applications.
- ESD/EMI Protection: Ensuring there are no disruptions from electrostatic discharge and electromagnetic interference is crucial for safe, reliable operation.
- Surge Protection: Safeguards need to be in place to suppress transients and prevent overvoltage.
- Fast Switching: Instrument clusters require fast and frequent switching and need components that can keep up without compromising speed or efficiency.
- Low Forward Voltage Drop: Maximizing efficiency is important for the instrument cluster and other automotive devices.
- Thermal Stability/Heat Dissipation: Optimal thermal performance is needed for safety and efficiency.
- Legibility: Ensuring the display is easily readable from a distance of 1-2 feet is critical, especially in varying lighting conditions such as direct sunlight or low light. This requirement underscores the importance of display clarity for safe operation.
- Applicable Industry Standards: For auto applications, components must adhere to stringent requirements, including AEC-Q101 qualification.
Recommended Products
Power Management |
||
Schottky Barrier Rectifier: SMD36HE1Q
|
Schottky Barrier Rectifier: SMD24PLQ
|
Schottky Barrier Rectifier: SK54AQ-L
|
Schottky Barrier Rectifier: SK56BQ-L
|
TVS: SMA6J60AQ
|
TVS: SMBJ60AQ
|
TVS: SMCJ14CAQ
|
TVS: SMF14AQ
|
|
Connectivity (CAN / LIN / Wireless) |
||
ESD Protection: ESD1524D3BHE3A
|
ESD Protection: ESD24VD3BHE3
|
ESD Protection: ESDSB5V0D3BHE3
|
Signal Conditioning & MUX |
||
ESD Protection: ESD12VD3BHE3
|
ESD Protection: ESDSB5V0D3BHE3
|
|
TVS: SMF5.0AQ
|
TVS: SMF12AQ
|
|
Display Module |
||
ESD Protection: ESDSB5V0D3BHE3
|
ESD Protection: ESDSLC3V3D3B
|
ESD Protection: SRV33-4L
|
ESD Protection: ESDLC3V3D5
|
|
|
Output Drivers |
||
MOSFET: 2N7002KDWBQ
|
MOSFET: SI2102AHE3
|
MOSFET: SI2310AHE3
|
MCC Semi has a broad range of discrete semiconductors to enhance the controllers in your automotive instrument cluster designs without sacrificing reliability or quality.
Explore our robust portfolio designed for excellence in automotive design:
On-board Charger (OBC)
EV Charging Station
Battery Management System (BMS)
DC-DC Converter
Advanced Driver Assistance System (ADAS)
Have questions? Use the MCC chatbot to contact us.
.png?width=50&height=50&name=mcc%20150x150%20(1).png)

%20(1).png)