Zener Diodes: How They Work and Where to Use Them
An Essential Guide to Voltage Regulation and Circuit Protection
What are Diodes ?
Diodes are two-terminal semiconductor devices that act as electrical check valves, allowing current to flow primarily in one direction. In forward bias, they conduct with a small voltage drop; in reverse bias, they block current, up to a limit.
Through material doping and structural design, different diode families are optimized for power conversion, high-speed switching, light emission, or voltage control.

Common Types of Diodes
- Rectifier Diodes: Efficient AC-to-DC power conversion
- Schottky Diodes: Low forward voltage drop, very fast switching
- LEDs: Electroluminescent light sources
- TVS Diodes: High-energy transient voltage suppression
- Zener Diodes: Stable, low-power voltage regulation and precise clamping
Understanding Zener Diodes
Zener diodes are designed to operate in reverse breakdown safely and predictably. When the reverse voltage reaches a specified level (the Zener voltage, Vz), the diode conducts to hold the voltage nearly constant. This makes Zeners ideal for reference rails, shunt regulators, level shifting, and input protection in analog, digital, and mixed‑signal designs.
.png?width=319&height=223&name=symbol%20variants%20zener%20diodes%20-%20mcc%20semi%20-%20micro%20commercial%20components%20(1).png)
What is a Zener Diode?
A Zener diode is a specialized semiconductor device designed to regulate voltage in electronic circuits. Unlike standard diodes that block reverse current, Zener diodes allow current to flow in reverse once a specific breakdown voltage, known as the Zener voltage (Vz), is reached. This controlled breakdown behavior makes them ideal for applications such as voltage regulation, overvoltage protection, and signal conditioning.

How Zener Diodes Work?
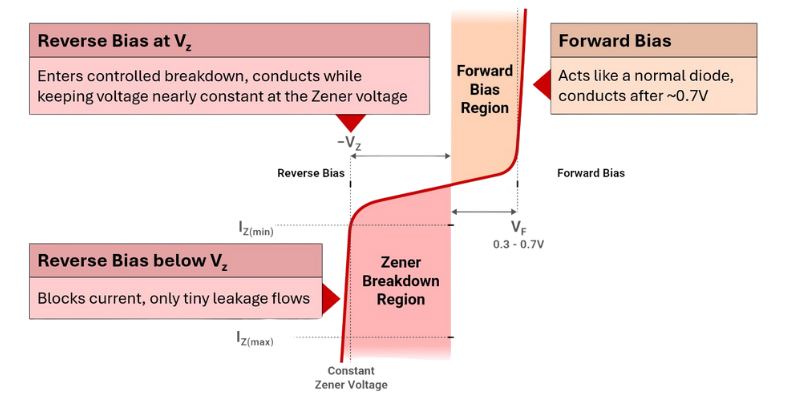
Zener diodes are designed to operate in both forward and reverse bias modes, but their unique functionality emerges when reverse biased. This behavior allows them to regulate voltage and protect circuits from overvoltage conditions.
Zener diodes operate differently depending on the biasing condition:
- Forward Bias: Behaves like a regular diode, conducting after ~ 0.7V.
- Reverse Bias Below Vz: Blocks current flow, allowing only minimal leakage.
- Reverse Bias at Vz: Enters controlled breakdown and maintains a stable voltage across the diode.
Breakdown Characteristics
When the reverse voltage exceeds the Zener voltage (Vz), the diode enters a breakdown region where it conducts while keeping the voltage nearly constant. This behavior is essential for voltage regulation and protection.
| Zener Breakdown (<5V) |
| Mechanism | 1. Quantum tunnelling in heavily doped diodes |
| Behavior |
1. Sharp “knee” in I-V curve 2. Negative temperature coefficient (Vz decreases with temperature) |
| Transition Zone (5V - 7V) |
| Mechanism | 1. Mixed Zener and Avalanche effects |
| Behavior |
1. Temperature coefficients nearly cancel 2. Ideal for precision voltage references (e.g. 6.2V Zener Diodes) |
| Transition Zone (5V - 7V) |
| Mechanism | 1. Impact ionization in moderately doped diodes |
| Behavior |
1. Gradual I-V curve “knee” 2. Positive temperature coefficient |
Why Use Zener Diodes?
Zener diodes offer key advantages that make them a reliable choice in analog and embedded systems. They provide consistent voltage regulation across varying conditions, which makes them ideal for low-power applications. Their simple two-terminal design requires minimal external components and fits easily into compact layouts. Zener diodes also react quickly to voltage spikes, protecting sensitive electronics. With a wide range of voltage ratings, packages, and power levels, they offer flexibility for diverse design needs. Their low cost, predictable performance, and broad application in areas such as signal conditioning, voltage clamping, and power sequencing make them a staple in both consumer and industrial electronics.
The key benefits of Zener diodes include:
- Stable Voltage Regulation under varying load conditions
- Fast Transient Response to voltage spikes
- Compact and Cost-Effective compared to IC regulators
- Precision Options with temperature compensation
- Low Standby Power consumption
- Easy Integration into analog and embedded designs
Applications of Zener Diodes
Zener diodes are versatile components used in a wide range of electronic applications. Their ability to maintain a fixed voltage and respond quickly to changes in circuit conditions makes them ideal for tasks such as voltage regulation, protection against overvoltage, and signal conditioning. Below are common use cases that highlight how Zener diodes enhance circuit performance and reliability.
How to Select the Right Zener Diode
Choosing the correct Zener diode for your application is essential to ensure reliable performance and circuit protection. Key factors such as breakdown voltage, power rating, package type, and temperature stability should be considered to match the diode to your design requirements.
When choosing a Zener diode, consider:
- Vz: Match to your desired regulation voltage
- Iz max: Must exceed expected load current
- Package: Thermal and mechanical suitability
- Temperature Stability: Crucial for precision circuits
- Power Rating: Ensure safe operation under load
MCC Zener Diode Portfolio
MCC provides a comprehensive selection of Zener diodes engineered to support a wide variety of electronic applications. Whether you're designing precision analog circuits, automotive systems, or compact embedded devices, MCC delivers reliable performance across multiple voltage ratings, package formats, and power levels.
Solutions include:
- Precision Zeners for analog references and sensors
- High-Current Zeners for industrial and automotive systems
- Low-Profile SMD Options for compact designs
- AEC-Q101 Qualified Parts for automotive-grade reliability
Zener diode Portfolio overview
MCC’s Zener diode portfolio is engineered to support a wide range of voltage regulation and protection needs across industries. From low-power precision circuits to high-current automotive systems, our product lineup offers flexibility in voltage ratings, package types, and performance characteristics.
Enhancing Sourcing Flexibility and Delivery Speed

MCC’s Vietnam manufacturing site strengthens our Zener diode portfolio with increased packaging capacity and improved global supply chain resilience. This expansion ensures faster delivery and greater sourcing flexibility for voltage regulation solutions.
- Largest MCC facility outside China supporting China+1 diversification
- Expanded package options: SOD-123, SOD-323, SOT-23
- Compact, high-reliability diodes for industrial and consumer applications
- Optimized logistics for shorter lead times and global availability
Additional Resources

Zener Diodes Guide
Our detailed guide offers an extensive overview of zener diodes, covering their core characteristics, key benefits, and applications examples.
Application Guides
Explore the broad range of applications for Zener diodes. From precision references and microcontroller rails to input clamping and surge suppression, MCC Zeners deliver stable regulation and fast protection across consumer, industrial, and automotive systems.
Complete Product Catalog
Explore our full range of Zener diodes engineered for precise voltage control in both forward and reverse directions. MCC’s cost-effective portfolio empowers engineers to design smarter with compact, reliable components.
Contact MCC for advanced solutions that deliver a competitive edge.
MCC is a manufacturer of high-quality discrete semiconductors to the consumer markets © MCC. All Rights Reserved · 2026