Understanding TVS Diodes:
A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding TVS Diodes
TVS diodes safeguard electronic systems from voltage spikes and transient surges. This informative guide explains everything you need to know about these mission-critical components.
What Are TVS Diodes?
Electronic devices — particularly miniaturized ones — are exposed to spikes in voltage caused by electrostatic discharge (ESD), lightning surges, power grid fluctuations, and even inductive switching events within the system. These transient events can be one-time occurrences or take place repeatedly.
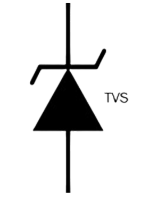
TVS diodes or transient voltage suppressors are components that protect sensitive electronics from harmful and potentially dangerous spikes in voltage. These semiconductor devices are meticulously engineered to preserve delicate electronics during sudden overvoltage.
Acting as tiny shields, TVS diodes:
- Protect electronic systems by limiting transient voltage spikes
- Safeguard delicate components from damage due to overvoltage
- Ensure the longevity and reliability of electronics by absorbing and dissipating excess energy during transient events
What Are TVS Diodes Used for?
The primary role of TVS diodes is to protect electronic systems by clamping transient voltage and diverting excess transient current away from the protected components, thereby maintaining reliable performance.
Because they ensure safe operation under varying environmental conditions, TVS diodes are crucial for a broad range of applications, including:
- Automotive: From the in-cabin infotainment center to the body control module (BCM) and safety features like advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS), TVS diodes are a must for surges and ESD protection to maintain automotive system reliability.
- Computing: Personal and professional computing devices and line signals require reliable protection from transient spikes that could cause system failure and data loss. TVS applications range from solid state drives and DC fans that cool notebooks and computers to uninterruptible power supplies (UPS) and DC-DC converters.
- Industrial: From smart energy meters to electrical panel switches for solar systems and robust machinery, industrial devices are vulnerable to transient spikes amid harsh environments.
- Consumer: TVS diodes are essential for a host of consumer devices that deliver convenience and productivity — from cordless power tools and class D amplifiers to eco-friendly cordless lawn mowers.
How Do TVS Diodes Work?
%20real%20transparent.png?width=600&height=350&name=Transient%20Voltage%20Suppressor%20also%20known%20as%20TVS%20-%20mcc%20semi%20-%20micro%20commercial%20components%20%20(600%20x%20350%20px)%20real%20transparent.png)
When the voltage exceeds the predetermined threshold the TVS diode detects this difference in nanoseconds, then “clamps” to divert the excess energy away from the circuit. The excessive transient current flows through the TVS back to the source, securing consistent voltage for the protected system.
After the surge is over, the TVS diode will automatically reset to its non-conducting state, ready to protect the circuit from the next unexpected surge.
TVS Diodes Provide Superior Overvoltage Protection
Compared to other overvoltage protection devices, including metal oxide varistors (MOV), thyristors, and gas discharge tubes (GDT), TVS diodes are commonly used due to their effective clamping mechanism and system level compatibility:

What Are the Advantages of TVS Diodes?
TVS diodes offer a range of benefits that make them indispensable in assuring the reliable operation of electronic systems. By absorbing and dissipating energy during transient events, TVS diodes also deliver the following advantages:
- Enhanced reliability: Effective protection against overvoltage ensures that electronic systems operate reliably, reducing the risk of unexpected failures.
- Improved safety: TVS diodes help decrease the risk of electrical fires and other hazards, enhancing the safety of electronic systems.
- Component longevity:TVS diodes help prolong the lifespan of sensitive components by safeguarding them from overvoltage incidents, reducing the need for frequent replacements.
- Industry compliance: High-quality TVS diodes guarantee that products meet stringent industry standards, which is particularly vital in sectors like automotive and aerospace.
- Cost-effectiveness: Preventing system failures and minimizing downtime results in significant cost savings regarding repairs and maintenance.
- Reduced interference: TVS diodes feature high impedance and noise attenuation, which minimize EMI in switching circuits often used in small electronics.
- Versatility: These diodes can be used in various applications to safeguard a wide range of electronic devices and systems.
TVS Diode Parameters

What is Clamping Voltage in TVS Diodes?
For TVS diodes, the breakdown voltage (VBR) is the point at which the diode begins to conduct and limit voltage at the clamping voltage (VC) level across protected components, preventing exposure to damaging spikes in voltage.
The combination of clamping voltage and the peak pulse current (IPP) should not exceed the peak pulse power (PPP) of the TVS. Otherwise, the TVS will suffer electrical overstress and this may result in damage or catastrophic failure.
A lower clamping voltage offers better protection but may introduce signal distortion. It’s best to consider all parameters carefully when selecting a TVS diode.
How Does a Clamping Voltage Diode Work?
A clamping voltage diode, commonly referred to as a transient voltage suppressor (TVS), plays an essential role in protecting electronic components from sudden voltage spikes. They achieve this by redirecting excess voltage, thereby safeguarding sensitive devices from damage.
Mechanism of Action
- Detection and Diversion: When there is a rapid increase in voltage, the clamping diode detects the surge and becomes conductive. This enables the diode to divert excess current away from sensitive components, thereby protecting them.
- Voltage Limitation: During conduction, the diode clamps the voltage to a predetermined safe level. This action shields the circuit from potentially harmful overvoltage effects.
- Rapid Response: TVS clamping diodes respond quickly to voltage transients, which is crucial for preventing even brief spikes from causing damage to vulnerable circuitry.
Benefits of Clamping Diodes
- Protection: They provide a reliable defense for electronics, ensuring longevity and functionality.
- Efficiency: Their swift response to voltage changes makes them more efficient than other protective components.
- Versatility: Clamping diodes are suitable for various applications, ranging from protecting household electronics to safeguarding industrial equipment.
In summary, clamping voltage diodes are crucial for maintaining the durability and resilience of electronic systems by offering essential protection against unexpected electrical surges.
What is Peak Pulse Power?
A TVS diode’s peak pulse power (PPP) is the maximum rate at which the electrical energy is transferred during a pulse without the TVS being damaged. Expressed in watts, peak pulse power is critical when selecting a TVS diode, and it indicates the diode’s ability to handle spikes and energy levels effectively to prevent damage to connected components and systems.
Peak pulse power is not to be confused with the peak pulse current (IPP). Peak pulse current is measured in amperes and represents the maximum amount of electrical current that flows during a pulse. A selected TVS should have a peak pulse current that exceeds the anticipated transient current to ensure the component can safely absorb the surge.
How Does TVS Diode Working Voltage Work?
The working voltage of a TVS diode is its normal operational state when the component is dormant and ready to react to an unexpected surge. If the voltage exceeds the diode’s breakdown voltage (VBR), the TVS immediately activates to divert additional current from the protected components.
Ensuring TVS Diode Reliability and Performance
The effective protection of sensitive electronic systems often hinges on the reliability and performance of the TVS diode used in the design. Understanding what could cause a TVS diode to fail, selecting the appropriate diode for your needs, and ensuring the correct parameters are essential steps in specifying the right component and maintaining system integrity.
Top Causes of TVS Diode Failure
Choosing the incorrect parameters or a low-quality TVS component can lead to dire consequences. The most common cause of TVS failure? Current flow that exceeds the diode’s peak pulse power rating.
When the TVS fails altogether or sustains significant damage, it can lead to:
- Severe damage to electronic systems
- Data loss
- System failures
- Fires and other safety hazards
- Unreliable system performance
- Increased maintenance costs
Selecting the Right TVS Diode
Here’s how to specify the right TVS for your project:
- Choose the reverse working voltage slightly higher than the system’s nominal voltage. Our experts recommend increasing the reverse working voltage (VRWM) slightly when choosing a TVS diode to avoid the avalanche breakdown stage. For example, a 12V line should be protected by a 14V TVS.
- Select a peak pulse power rating based on testing requirements and environmental conditions.
- Choose the package best-suited for your size, power, and form factor needs.
Applying TVS Diodes in Hot-Swap Systems
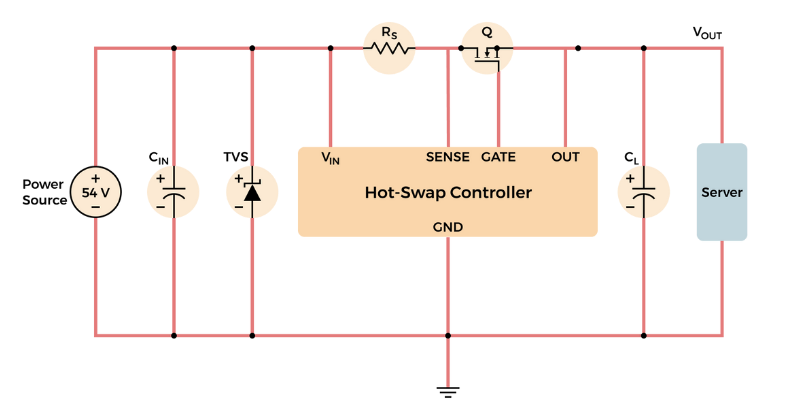
Hot-swap designs, especially in data centers, require careful TVS diode selection to handle transient voltage surges during board swaps. Using a clear, step-by-step method helps ensure the diode effectively clamps spikes and protects sensitive components—boosting system reliability and preventing costly downtime. Learn more about best practices for integrating TVS diodes in hot-swap systems here.
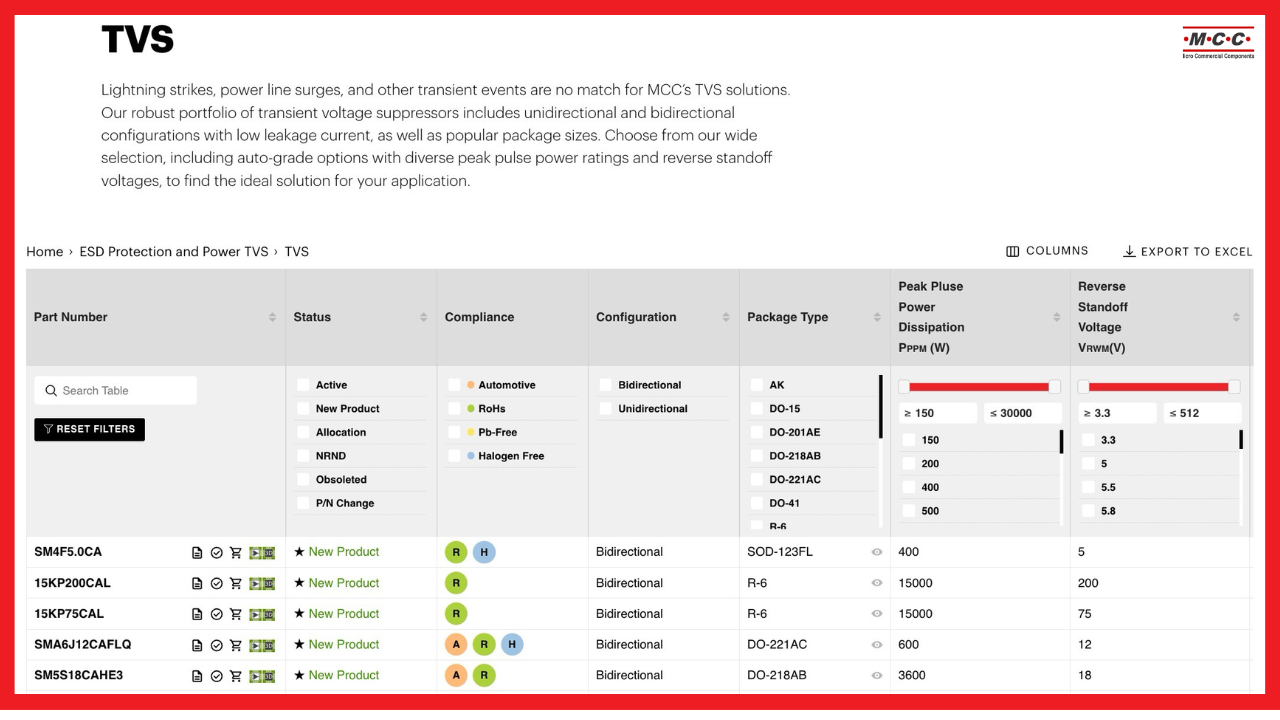
TVS Diodes Are Available in a Wide Variety of Packages
TVS diodes are available in diverse packages to suit various applications. The most popular options for protecting electronics against transient events are SMA, SMC, SMB, SOD-123, and SOD-323.
MCC offers a broad range of TVS packages and mounting types:
Low-Profile TVS Packages

Our low-profile surface-mount devices (SMD) are available in popular SOD-123FL packages, as well as DO-221AC and SMBF.
Surface-Mount TVS Packages
MCC’s surface-mount TVS components are available in diverse package options like SMA, SMB, SMC, and DO-218AB.

High-Power TVS Packages
High-power applications are met with robust packages including SMG, SME, and the AK series with peak currents from 1K to 15K.
Axial Leaded TVS Diode Packages
Ideal for specialized design requirements, MCC also offers axial leaded packages ranging from the compact DO-41 to larger R6 options.
Each package offers specific benefits in size, power capacity, and form factor, ensuring seamless integration into a broad range of electronic systems.

Explore MCC's Diverse Range of TVS Diodes
MCC offers a comprehensive selection of TVS diodes to meet various application and power needs. Our robust lineup of TVS components features more than 4,000 products, with new TVS components introduced regularly.
Strengthening Supply Chain Resilience for TVS Components

MCC’s Vietnam facility boosts TVS diode production to meet growing demand for surge protection solutions. This strategic expansion ensures improved regional responsiveness and greater sourcing flexibility for global customers.
- Largest MCC facility outside China supporting China+1 diversification
- Expanded package options: SMA, SMB, SMC, SOD-123FL
- High-performance TVS diodes for industrial and consumer applications
- Faster delivery timelines and strengthened supply chain resilience
MCC’s Non-Automotive TVS Products
For industrial, commercial, and computing applications, our selection of TVS diodes features handling power from 200W to 6,000W. These diodes are available in packages from SOD-123 and SMA to innovative SMB options with power up to 2000W.
We meet high-power demands with TVS solutions ranging from 15kW to 30kW, making them ideal for challenging environments with strong transient interference. Our high-power TVS diodes include the AK series, fully tested for peak currents following UL and IEC industry standards.
MCC’s Robust Auto-Grade TVS Diode Portfolio
Nearly half of our TVS portfolio (40%) is tailored to meet the stringent requirements of automotive applications, including AEC-Q101 qualification. These diodes feature peak pulse power ratings from 200W to 6,600W and are available in a variety of SMD packages. Our automotive components undergo rigorous testing from advanced facilities to ensure uncompromising quality and performance.
TVS diodes are a must when it comes to protecting sensitive electronics by mitigating transient spikes. However, a deep understanding of their function and specifications is required for seamlessly integrating these diodes into your designs for maximum performance and reliability.
No matter the application or design parameters, MCC has reliable TVS solutions to meet any need.
MCC's Non-Automotive TVS
| PPP (W) | Configuration | Package | Family Series | VRWM (V) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 200 | Bi-dir | SOD-123FL | SMF | 5 ~ 170 |
| Uni-dir | SOD-123FL | SMF | 5 ~ 170 | |
| Uni-dir | SOD-123HL | SMH | 5 ~ 100 | |
| 400 | Bi-dir | SOD-123FL | SM4F | 5 ~ 45 |
| Bi-dir | DO-221AC | SMAF | 5 ~ 300 | |
| Bi-dir | SMA | SMAJ | 5 ~ 440 | |
| Bi-dir | SMA | SMAJP4KE | 5.8 ~ 495 | |
| Bi-dir | SMA | SMAJS | 24 | |
| Uni-dir | SOD-123HL | SM4H | 5 ~ 100 | |
| Uni-dir | SOD-123FL | SM4F | 5 ~ 100 | |
| Uni-dir | DO-221AC | SMAF | 5 ~ 300 | |
| Uni-dir | SMA | SMAJ | 5 ~ 440 | |
| Uni-dir | SMA | SMAJP4KE | 5.8 ~ 495 |
| PPP (W) | Configuration | Package | Family Series | VRWM (V) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 | Uni-dir | SMB | SMBSAC | 5 ~ 50 |
| 600 | Bi-dir | DO-221AC | SMA6J..FL | 11 ~ 85 |
| Bi-dir | SMBF | SMBF | 5 ~ 220 | |
| Bi-dir | SMA | SMA6J | 5 ~ 58 | |
| Bi-dir | SMB | SMBJ | 5 ~ 440 | |
| Bi-dir | SMB | SMBJ..L | 220 ~ 440 | |
| Bi-dir | SMB | SMBJP6KE | 5.8 ~ 468 | |
| Uni-dir | DO-221AC | SMA6J..FL | 5 ~ 130 | |
| Uni-dir | SMBF | SMBF | 5 ~ 220 | |
| Uni-dir | SMA | SMA6J | 5 ~ 58 | |
| Uni-dir | SMB | SMBJ | 5 ~ 440 | |
| Uni-dir | SMB | SMBJ..L | 220 ~ 440 | |
| Uni-dir | SMB | SMBJP6KE | 5.8 ~ 468 | |
| Uni-dir | SMB | SMBJP6KE..L | 214 ~ 342 |
MCC's Non-Automotive TVS
| PPP (W) | Configuration | Package | Family Series | VRWM (V) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1000 | Bi-dir | SMB | SMB10J | 5 ~ 120 |
| Bi-dir | SMB | SMBJ1.0KE | 5.8 ~ 77.8 | |
| Uni-dir | SMB | SMB10J | 5 ~ 120 | |
| Uni-dir | SMB | SMBJ1.0KE | 5.8 ~ 77.8 | |
| 1500 | Bi-dir | SMB | SMB15J | 15 ~ 58 |
| Bi-dir | SMC | SMCJ1.5KE | 5.8 ~ 495 | |
| Bi-dir | SMC | SMCJ | 5 ~ 440 | |
| Uni-dir | SMB | SMBJ15J | 15 ~ 58 | |
| Uni-dir | SMC | SMCJ1.5KE | 5.8 ~ 495 | |
| Uni-dir | SMC | SMCJ | 5 ~ 440 | |
| 2000 | Bi-dir | SMB | SMB20J | 20 ~ 58 |
| Uni-dir | SMB | SMBJ20J | 20 ~ 58 | |
| 3000 | Bi-dir | SMC | SMLJ | 5 ~ 440 |
| Uni-dir | SMC | SMLJ | 5 ~ 440 | |
| 5000 | Bi-dir | SMC | 5.0SMLJ | 11 ~ 400 |
| Uni-dir | SMC | 5.0SMLJ | 11 ~ 400 |
| PPP (W) | Configuration | Package | Family Series | VRWM (V) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 400 | Bi-dir | DO-41 | P4KE(5.8~495) | 5.8 ~ 495 |
| Uni-dir | DO-41 | P4KE(5.8~495) | 5.8 ~ 495 | |
| 500 | Bi-dir | DO-15 | P5KE(5~200) | 5 ~ 200 |
| Bi-dir | DO-15 | SA(5~170) | 5 ~ 170 | |
| Uni-dir | DO-15 | P5KE(5~200) | 5 ~ 200 | |
| Uni-dir | DO-15 | SA(5~170) | 5 ~ 170 | |
| 600 | Bi-dir | DO-15 | P6KE(5.8~512) | 5.8 ~ 512 |
| Uni-dir | DO-15 | P6KE(5.8~512) | 5.8 ~ 512 | |
| 1500 | Bi-dir | DO-201AE | 1.5KE(5.8~467) | 5.8 ~ 467 |
| Uni-dir | DO-201AE | 1.5KE(5.8~467) | 5.8 ~ 467 | |
| Uni-dir | DO-201AE | LCE(6.5~28) | 6.5 ~ 28 | |
| 3000 | Bi-dir | R-6 | 3KP(5~220) | 5 ~ 220 |
| Uni-dir | R-6 | 3KP(5~220) | 5 ~ 220 | |
| 5000 | Bi-dir | R-6 | 5KP(5~440) | 5 ~ 440 |
| Bi-dir | R-6 | 5KP..L(22~188) | 22 ~ 188 | |
| Uni-dir | R-6 | 5KP(5~440) | 5 ~ 440 | |
| Uni-dir | R-6 | 5KP..L(22~188) | 22 ~ 188 | |
| 6000 | Bi-dir | R-6 | SLD(10~60) | 10 ~ 60 |
| Uni-dir | R-6 | SLD(10~60) | 10 ~ 60 |
MCC's High-Power TVS
| PPP (W) | Configuration | Package | Family Series | VRWM (V) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15000 | Bi-dir | R-6 | 15KP(17~280) | 17 ~ 280 |
| Bi-dir | R-6 | 15KP..L(17~280) | 17 ~ 280 | |
| Uni-dir | R-6 | 15KP(17~280) | 17 ~ 280 | |
| Uni-dir | R-6 | 5KP..L(17~280) | 17 ~ 280 | |
| 30000 | Bi-dir | R-6 | 30KP(28~288) | 28 ~ 288 |
| Uni-dir | R-6 | 30KP(28~288) | 28 ~ 288 |
| IPP (A) | Configuration | Package | Family Series | VRWM (V) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1000 | Bi-dir | AK | AK1(76) | 76 |
| 2500 | Bi-dir | SMG | SMGJ(80) | 80 |
| 3000 | Bi-dir | AK | AK3(30~430) | 30 ~ 430 |
| 6000 | Bi-dir | AK | AK6(58~430) | 58 ~ 430 |
| 10000 | Bi-dir | SME | SMEJ(58~86) | 58 ~ 86 |
| Bi-dir | AK | AK10(58~430) | 58 ~ 430 | |
| 15000 | Bi-dir | AK | AK15(58~76) | 58 ~ 76 |
MCC's Automotive TVS
| PPP (W) | Configuration | Package | Family Series | VRWM (V) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 200 | Bi-dir | SOD-123FL | SMF..Q | 5 ~ 100 |
| Uni-dir | SOD-123FL | SMF..HE3 | 5 ~ 100 | |
| Uni-dir | SOD-123FL | SMF..Q | 5 ~ 100 | |
| 400 | Bi-dir | SOD-123FL | SM4F..HE3 | 6 ~ 45 |
| Bi-dir | SMA | SMAJ..HE3 | 5 ~ 190 | |
| Bi-dir | SMA | SMAJ..Q | 5 ~ 190 | |
| Bi-dir | SMA | SMAJP4KE..HE3 | 10.2 ~ 185 | |
| Bi-dir | SMA | SMAJP4KE..Q | 5.8 ~ 185 | |
| Uni-dir | SOD-123FL | SM4F..HE3 | 6 ~ 100 | |
| Uni-dir | SMA | SMAJ..HE3 | 5 ~ 190 | |
| Uni-dir | SMA | SMAJ..Q | 5 ~ 190 | |
| Uni-dir | SMA | SMAJP4KE..HE3 | 10.2 ~ 185 | |
| Uni-dir | SMA | SMAJP4KE..Q | 5.8 ~ 185 |
MCC's Automotive TVS
| PPP (W) | Configuration | Package | Family Series | VRWM (V) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 600 | Bi-dir | DO-221AC | SMA6J..FLQ | 5 ~ 85 |
| Bi-dir | SMA | SMA6J..HE3 | 10 ~ 100 | |
| Bi-dir | SMA | SMA6J..Q | 10 ~ 20 | |
| Bi-dir | SMB | SMBJ..HE3 | 5 ~ 190 | |
| Bi-dir | SMB | SMBJ..Q | 5 ~ 190 | |
| Bi-dir | SMB | SMBJP6KE..HE3 | 10.2 ~ 185 | |
| Bi-dir | SMB | SMBJP6KE..Q | 5.8 ~ 185 | |
| Uni-dir | DO-221AC | SMA6J..FLQ | 5 ~ 85 | |
| Uni-dir | SMA | SMA6J..HE3 | 10 ~ 100 | |
| Uni-dir | SMA | SMA6J..Q | 10 ~ 100 | |
| Uni-dir | SMB | SMBJ..HE3 | 5 ~ 190 | |
| Uni-dir | SMB | SMBJ..Q | 5 ~ 190 | |
| Uni-dir | SMB | SMBJP6KE..HE3 | 10.2 ~ 185 | |
| Uni-dir | SMB | SMBJP6KE..Q | 5.8 ~ 185 |
| PPP (W) | Configuration | Package | Family Series | VRWM (V) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1500 | Bi-dir | SMC | SMCJ1.5KE..HE3 | 10.2 ~ 185 |
| Bi-dir | SMC | SMCJ1.5KE..Q | 5.8 ~ 185 | |
| Bi-dir | SMC | SMCJ..HE3 | 10 ~ 190 | |
| Bi-dir | SMC | SMCJ..Q | 5 ~ 190 | |
| Uni-dir | SMC | SMCJ1.5KE..HE3 | 10.2 ~ 185 | |
| Uni-dir | SMC | SMCJ1.5KE..Q | 5.8 ~ 185 | |
| Uni-dir | SMC | SMCJ..HE3 | 10 ~ 190 | |
| Uni-dir | SMC | SMCJ..Q | 5 ~ 190 | |
| 3000 | Bi-dir | SMC | SMLJ48..HE3A | 10 ~ 48 |
| Bi-dir | SMC | SMLJ..Q | 5 ~ 48 | |
| Uni-dir | SMC | SMLJ48..HE3A | 10 ~ 48 | |
| Uni-dir | SMC | SMLJ..Q | 5 ~ 48 | |
| 5000 | Bi-dir | SMC | 5.0SMLJ..HE3 | 5 ~ 85 |
| Uni-dir | SMC | 5.0SMLJ..HE3 | 5 ~ 85 | |
| 6600 | Bi-dir | DO-218AB | SM8S..HE3 | 14 ~ 43 |
| Uni-dir | DO-218AB | SM8S..HE3 | 10 ~ 43 |
Additional Resources

TVS Diodes Brochure
Our detailed brochure offers an extensive overview of TVS Diodes, covering their characteristics, benefits, and the latest advancements in the field.
Applications
Explore the broad spectrum of applications for TVS Diodes. From consumer electronics to automotive systems, see how these components can boost the performance and reliability of your products.
TVS Diodes Catalog
Effortlessly browse our comprehensive catalog to find the right TVS Diodes for your needs. Detailed specifications and comparisons assist you in choosing with confidence.
Contact MCC for advanced solutions that deliver a competitive edge.
MCC is a manufacturer of high-quality discrete semiconductors to the consumer markets © MCC. All Rights Reserved · 2026